Control of a Novel Omnidirectional Handsfree Wheelchair Design in the form of a Sel-Balancing Ballbot (August 2022 – Present)
Graduate Students: Mahshid Mansouri, Keona Banks, Tianyi Han, Yixiao Liu
Faculty: Elizabeth T. Hsiao-Wecksler, Bob Norris, Joao Ramos, Deana McDonagh
Our team is working on a novel personal mobility device, i.e., PURE (Personalized Unique Rolling Experience), that would provide a new way for hands-free mobility along with omnidirectional capability (i.e., able to move forward/backward, slide left/right, and spin in place). The drivetrain of PURE is a ball-based robot (ballbot), which rides on top of a spherical wheel or ball. This unique omnidirectional design allows the user to travel in any direction simply by leaning the torso toward the desired direction without using hands (i.e., lean-to-steer hands-free control). It can also be controlled using a traditional joystick if desired. Segway scooters also use lean-to-steer control; however, for those devices, the rider must be able to shift their center of mass far enough to cause the scooter to move. We have added the Torso-dynamics Estimation System (TES), which consists of an instrumented seat (Force Sensing Seat – FSS) and a sensor (inertial measurement unit, IMU) worn on the chest to measure and amplify the torso motions of the rider to control the device. Thus, riders with reduced trunk function can still control the device. A major target population for PURE is manual wheelchair users, as they generally have sufficient trunk function.
To date, two ballbot drivetrain chassis prototypes (Gen 1 and Gen 2) have been developed. Gen 2 is able to carry riders weighing up to 60 kg and a maximum speed of 2.3 m/s. We are in the process of incorporating advanced control options, such as driver assistance for obstacle detection and response can accelerate operator training, improve the driving experience, and reduce operator attentional demand. The current prototype has only been operated on level and even indoor surfaces. Future work is needed to allow PURE to operate on other level, uneven surfaces, such as grass, gravel, and sidewalks.
State Anxiety Detection and Monitoring Using Multimodal Wearables Sensors: Wear Study (August 2022 – Present)
Graduate Students: Maxine He, Abdul Alkurdi
Faculty: Manuel Hernandez, Elizabeth T. Hsiao-Wecksler, Richard Sowers, and Jean Clore
Funding: Jump ARCHES (Applied Research for Community Health through Engineering and Simulation) program, a joint program between OSF HealthCare and UIUC
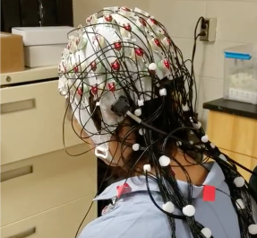
Mental health is integral to overall well-being, deeply intertwined with physical health and quality of life. As more individuals face challenges related to stress, anxiety, depression, and other mental disorders, developing robust mental health monitoring methods has never been more critical. University students, in particular, face a unique blend of stressors that can significantly impact their mental and emotional well-being, such as academic pressure, financial burden, social stress, career anxiety, etc. By understanding the effects of stress and anxiety on university students and developing reliable mental health monitoring tools, we can take active steps to manage and reduce stress, enhancing the overall university experience.
With this in mind, we extend beyond the RADWear study to the WEAR study, which focuses on stress/anxiety detection in UIUC students in STEM fields (with an emphasis on women and underrepresented minority groups) and Carle Illinois students. The WEAR study consists of 2 in-lab sessions and a 2-week remote data collection in between in-lab sessions. We utilize a battery of sensor modalities such as electroencephalogram (EEG), electromyography (EMG), research-grade electrocardiogram (ECG), and Galvanic skin response (GSR) sensor, in conjunction with two wearables (Hexoskin smart shirt and Empatica E4 wristband), to comprehensively capture the physiological responses elicited by various types of stressors in a lab-controlled condition. Then, similar to the RAD-Wear study, participants will be given Hexoskin and E4 to remotely collect physiological data in 2 weeks, hoping to capture anxiety/stress induced in real-world scenarios (e.g., examinations, interviews, and presentations). As part of Maxine’s dissertation, she will explore patterns of physiological responses (particularly EEG and ECG) to different types of stressors, the interplay between brain and cardiac activities, and multimodal (generalized or personalized) stress/anxiety detection using machine learning algorithms. Eventually, we hope this project sheds light on understanding the underlying mechanism of stress/anxiety and promoting mental health by developing reliable mental health monitoring techniques.
Remote State Anxiety Detection and Monitoring Using Multimodal Wearables Sensors: RAD-Wear Study (Jul 2021 – Present)
Graduate Students: Maxine He, Abdul Alkurdi
Faculty: Manuel Hernandez, Elizabeth T. Hsiao-Wecksler, Richard Sowers, and Jean Clore
Funding: Jump ARCHES (Applied Research for Community Health through Engineering and Simulation) program, a joint program between OSF HealthCare and UIUC
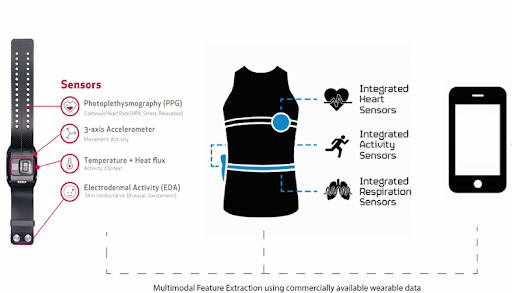
Mental health disorders are prevalent in the worldwide population, and the COVID-19 pandemic during the past years has been shown associated with an increased incidence of mental disorders, such as insomnia, distress, depression, and anxiety. Anxiety and stress negatively impact both psychological and physical health, and medical trainees are at increased risk for mental health problems even during normal times, let alone when faced with a pandemic. In addition, it is particularly difficult for healthcare professionals to access mental health services due to schedule conflicts, social stigma, and other obligations. Therefore, this study has proposed to use of multimodal smart wearables to detect and monitor the state anxiety of healthcare trainees to examine the reliability and feasibility of wearable sensors application and the association between mental and physical well-being and pandemics. Namely, the Hexoskin smart shirt and Empatica E4 wristband are used to collect physiological signals, including heart rate, skin conductance, body temperature, breathing rate, and physical activity (based on 3-axis accelerometers). This study plans to recruit Phase 2 medical students from the University of Illinois College of Medicine at Peoria and have them wear the shirt and wristband for two 2-week periods and at least 6 hours per day. Meanwhile, a daily self-reported evaluation of their emotional states will be given and serve as the ground truth for state anxiety detection. We aim to explore the variations of stress levels in medical students during their rotations and implement robust machine learning algorithms to reliably detect the onset of anxiety in real-world scenarios.
Development and Clinical Evaluation of an Upper Limb Robotic Medical Education Training Simulator for Rigidity and Spasticity Assessment (May 2021 – Nov 2022)
Graduate Students: Mahshid Mansouri, Yinan Pei
Faculty: Elizabeth T. Hsiao-Wecksler, Christopher M. Zallek
Funding: Jump ARCHES (Applied Research for Community Health through Engineering and Simulation) program, a joint program between OSF HealthCare and UIUC. UIUC Grainger College of Engineering, ZJU-UIUC Institute Research Program.

The goal of this project was to develop an upper arm robotic training simulator as a medical education tool that could be used as a practice patient in healthcare settings to teach medical trainees how to assess and diagnose different abnormal muscle behaviors such as rigidity and spasticity (which are common in patients with Parkinson’s disease, strokes, multiple sclerosis, etc.). Rather than practicing on real patients, medical trainees could use this task trainer as a tool to practice different examination techniques and also be able to grasp the subtle differences between rigidity and spasticity.
In this project, Mahshid worked with another graduate student, Yinan, where we developed a controller to be able to replicate the torque profile that is observed in rigidity and spasticity behaviors to deliver the haptic feeling of these abnormal muscle behaviors seen in real patients. In addition, we worked together on the clinical evaluation of the task trainer to understand how realistic the two behaviors are being replicated by asking clinicians to provide feedback on different aspects of the simulation.
Link to published work for this project:
Design and Validation of a Soft Robotic Cardiac Transseptal Puncture Simulator
Graduate Student: Nicholas Thompson
Faculty: Elizabeth T. Hsiao-Wecksler, Girish Krishnan, and Abraham Kocheril
Funding: Jump ARCHES (Applied Research for Community Health through Engineering and Simulation) program, a joint program between OSF HealthCare and UIUC
Atrial fibrillation (AF) ablation, a surgical procedure used to treat AF, includes a process known as transseptal puncture, wherein the left atrium of the heart is accessed by mechanically puncturing the interatrial septum from the right atrium. Transseptal puncture is used in an increasing number of other cardiac procedures, such as left atrial appendage occlusion and mitral valve repair. Currently, the training process is through a set of visual fluoroscopy or ultrasound images in the virtual realm with no force feedback. However, skilled surgeons typically isolate the puncture zone by judging the force feedback felt through their catheters when in contact with the septum.
This project includes the design, assembly, and validation of a soft robotic transseptal puncture training simulator. The device replicates the dynamics of the right atrium using fiber-reinforced soft pneumatic actuators with an elastomeric anatomical representation of the right atrium. Simulated intracardiac echocardiography (ICE) imaging will familiarize users with the imaging technology used during the real procedure. Dynamics of the simulator will be validated against measured atrial volume change during atrial systole. The simulator will be evaluated for realism by clinical experts in transseptal puncture following completion.
Autonomous Morphing Bed Mattress for ALS Patients with Limited Movement Ability
Graduate Student: Mahshid Mansouri, Sandra Edward
Faculty: Elizabeth T. Hsiao-Wecksler, Girish Krishnan, Deana McDonagh, Christopher M. Zallek, Girish Krishnan
Funding: Jump ARCHES (Applied Research for Community Health through Engineering and Simulation) program, a joint program between OSF HealthCare and UIUC
ALS (Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis) is a progressive neurodegenerative disease that affects nerve cells in the brain and the spinal cord. The progressive degeneration of the motor neurons in ALS eventually leads to their demise. When the motor neurons die, the ability of the brain to initiate and control muscle movement is lost, which will lead to muscle weakness, disability, and eventually death. Patients with limited movement ability, e.g., caused by advanced-stage ALS, frailty due to aging, obesity, coma, or spinal cord injury, are not able to independently adjust their body position to relieve pressure ulcers. The standard of care is to use passive or active pressure-relieving bed mattresses and frequency repositioning to help alleviate pressure ulcers. The manually-intesnsive repositioning, transferring, and lifting of patients can result in patient injuries (abraision, falls) and are a leading cause of musculoskeletal injury to caregivers. Currently available active bed mattresses provide pressure relief to large body regions, but cannot offloading of specific pressure ulcer locations.
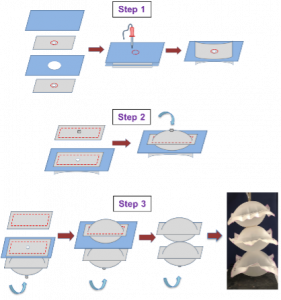
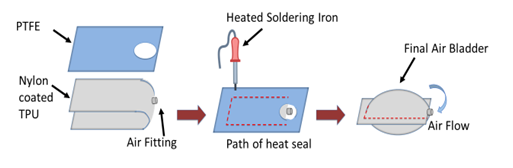
For this project, Mahshid worked with her lab mate, Sandra. The goal is to characterize and understand the behavior of a type of pneumatic soft actuator called air bladders. We have developed a CNC heat-sealing machine which we use to fabricate soft TPU (extensible) and Nylon TPU-coated (non-extensible) air bladders. So far, we have done a series of pressure-displacement experiments on both single and stacked air bladders in different sizes and shapes to understand how the height of the air bladders changes as a function of its internal pressure while it is inflated, and how various design variables such as the air bladder size, shape, material, manufacturing technique, etc. affect the displacement-pressure relationship. Meanwhile, we are working on developing simple analytical models of air bladders as well. The results of characterization experiments and analytical modelings can be used as design guidelines for engineers to better design pneumatic soft actuators for different applications, such as designing soft wearable devices.
Link to published work for this project:
Design Of A Passive Hydraulic Simulator For Biceps Spasticity Replication
Graduate Students: Yinan Pei, Jiahui Liang (former)
Faculty: Elizabeth T. Hsiao-Wecksler, Randy H. Ewoldt, Steven R. Tippett, Christopher M. Zallek
Funding: Jump ARCHES (Applied Research for Community Health through Engineering and Simulation) program, a joint program between OSF HealthCare and UIUC
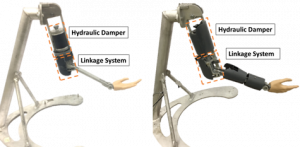
Spasticity is an abnormal muscle hypertonia behavior, affecting more than 12 million people respectively worldwide and usually associated with the brain lesion caused by spinal cord injuries, strokes, cerebral palsy, etc. The presence of these abnormal muscle behaviors will cause involuntary movements that hinder daily activities and affect the quality of life. The current assessment method for spasticity that relies on qualitative scales, such as the Modified Ashworth Scale (MAS), generally has poor inter-rater reliability rising from its subjective nature. It is crucial for students training for healthcare professions that evaluate patients with spasticity to have a clear understanding of different levels of spasticity and to gain sufficient hands-on assessment experiences. Current methods are inconsistent due to variability in training and limited availability of practice patients. Therefore, there is a clear need to develop a spasticity training simulator that can provide realistic and consistent replication of spasticity at different levels to minimize the need for practice patients.
The goal of this study was to develop a passive upper extremity simulator that can consistently replicate biceps spasticity in the elbow at different levels and be used to train future clinicians. Two generations of the simulator prototype have been developed. The first-generation prototype was capable of replicating most aspects of spasticity at MAS levels 0-4 and the second-generation added more design features to replicate subtle clinical signs of spasticity, such as variable catch angle, reduction in ROM, etc. A clinical evaluation study with a group of experienced clinicians will be conducted to validate the performance/realism of the second-generation training simulator.
Design, Validation, and Testing of a Wearable Device: Position, Velocity, Resistance Meter (PVRM)
Graduate Students: Leo (Seung Yun) Song
Faculty: E.T. Hsiao-Wecksler, Christopher Zallek, Steven R. Tippet
Funding: Jump ARCHES (Applied Research for Community Health through Engineering and Simulation) program, a joint program between OSF HealthCare and UIUC
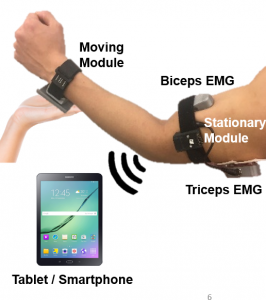
We are developing a wearable and ergonomic device (PVRM) to quantify passive arm movement of people with abnormalmuscle behavior. A clinician would attach the PVRM on the patient’s arm and perform a manually move the patient’s arm while recording the arm movement data. This project involves a diverse interdisciplinary team of engineers from Human Dynamics and Control Lab, industrial designers from the art and design department, physical therapy students/faculty from Bradley University, and clinicians from Illinois Neurological Institute.
The Biomechanical Consequences of Body Size Differences in Humans
Graduate Student: Maria Fox
Faculty: E. T. Hsiao-Wecksler, J. D. Polk
Modern humans display a wide range of variation in body size and shape. While all humans practice bipedalism in essentially the same way, it is unclear how these vast differences in body size affect locomotor performance and activity. This project will evaluate the functional consequences of body size in humans through a lab-based biomechanics study of 80 short and tall male and female subjects and a bone microstructure analysis of 30 femora and tali. Previous studies of scaling patterns in mammals suggest that size-related differences will be present in three major areas: 1) specific locomotor events during walking and running gait, 2) general changes throughout the gait cycle or activity, and 3) trabecular and subchondral bone properties. Data from standing, walking, and running trials will be collected from a 6-camera Qualisys 3D motion capture system and force plates (AMTI, Bertec instrumented treadmill). These kinematic and kinetic data are used to evaluate posture and limb flexion, relative force production, and leg spring stiffness at specific points during gait. They may also be used to assess stride length and frequency, angular excursion, and balance throughout walking/running and standing trials. Analyses of bone microstructure will reveal patterns of habitual loading and posture. These data indicate whether small and large individuals employ different mechanisms to remain upright and locomote bipedally through the world, as well as whether they have implications for the activity and behavior practiced by our hominin ancestors.
Graduate Students: Ayush Sinha
Faculty: E.T. Hsiao-Wecksler, G. Krishnan
Upper-body model and pneumatic controller for easy testing.
Pneumatic Sleeve Orthosis for Loftstrand Crutches: Application of Soft Pneumatic FREE Actuator
Graduate Students: C. Xiao, G. Singh, Y. Oo, D. Farooq
Faculty: E.T. Hsiao-Wecksler, G. Krishnan
While walking with crutches, peak loads observed in the wrist and palm can approach 50% of body weight and the wrist can experience extreme hyperextension. The repetitive, high loads and poor wrist postures associated with crutch use have been shown to lead to joint pain and injury, carpal tunnel syndrome, arthritis, or joint deformity. To address these issues, we are developing a light weight, pneumatically-powered forearm orthosis to improve wrist posture and reduce loads in the wrist and palm while using Lofstrand, or forearm, crutches. Lofstrand crutches tend to be used by people that need long-term gait assistance. We designed a pneumatic sleeve that is attached to the forearm cuff of the crutch. The user inserts the forearm into the sleeve, which can be actuated to constrict about the forearm. Thus, some of the body weight load would be redirected to the cuff of the crutch via the sleeve, instead of the entire load going into the crutch handle via the wrist and palm. The constriction force is created by pressurizing a custom-fabricated McKibben pneumatic muscle actuator that was wrapped around rigid splints attached to the crutch cuff. This custom McKibben muscle is one embodiment of a Fiber Reinforced Elastomeric Enclosure (FREE) actuator. FREE actuators can be constructed to produce a variety of motion patterns (constriction, expansion, rotation, and coiling). To produce a self-contained system to pressurize the sleeve, we are developing a method to harvest pneumatic energy from the crutch during walking. The goal is to use a custom piston pump in the crutch tip and store pressurized air into an elastomeric accumulator housed in the crutch shaft. The pump is also expected to operate as a shock absorber to mitigate impulse loading on the body.
Design of a Universal Instrumented Wheelchair Hand Rim
Graduate Students: A. Gaglio
Faculty: E.T. Hsiao-Wecksler
Collaborators: IntelliWheels, Inc., B. Slavens, I. Rice
Approximately 3.26 million Americans are wheelchair bound and an estimated 83% of this population are manual wheelchair users (MWUs). MWUs exhibit a high incidence of self-reported shoulder pain that increases with duration of wheelchair use and is attributed to excessive mechanical loading of the glenohumeral (shoulder) joint during wheelchair locomotion. Various modified wheelchair systems have been developed to ease upper extremity work during wheelchair locomotion including powered, push-assisted, lever-driven, and geared wheelchairs. In collaboration with IntelliWheels, Inc. and the University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee, we are designing an instrumented wheelchair hand rim that may be used with both geared and non-geared wheelchair wheels. This device measures the forces and torques at the point of application of the hand on the hand rim as well as wheel kinematics throughout locomotion. This information could provide new insight into the As the first instrumented hand rim for geared wheelchair wheels, this device could validate our hypothesis that gearing manual wheelchair wheels provides users a nonintrusive method to prevent overuse induced injuries in the upper extremities.
Fluid Power Assistive Orthoses
E. T. Hsiao-Wecksler, A. Alleyne, E. Loth
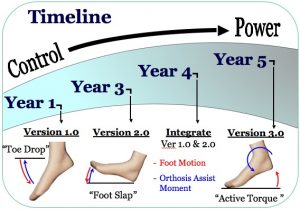
In the US alone, there are over 800,000 individuals affected by gait disabilities caused by weakness of muscle groups below the knee. This project, which is a test bed project for the NSF funded Engineering Research Center for Compact and Efficient Fluid Power, will design novel ankle foot orthoses (AFOs) with embedded fluid power control and actuation that assist a person’s functional gait. Each design iteration will address progressively more complex gait pathologies, thus allowing for an evolution of advanced fluid power concepts, such as power harvesting and fast-response sensing. Initial designs will utilize fluid-controlled (adaptive-passive) systems to correct for toe drop and foot slap, helping to lift the foot during swing and initial foot contact during walking. Later advanced designs will use fluid-powered (active) systems to provide torque assistance during the propulsive late-stance phase of the gait cycle. The testbed will demonstrate and integrate compact, efficient, and effective fluid power concepts in a challenging, un-tethered, human-scale device. The long term goal is to develop and test a series of prototype devices that will incorporate current thrust area projects, as well as drive new enabling and systems technologies within the center. These technologies will follow an evolutionary roadmap addressing the highest priority aspects of the overall testbed first and then integrating developments from other center projects as they come available over the lifetime of the center. This testbed will culminate with prototypes supplied to health care professionals and patients for testing and evaluation. This is a collaborative project with faculty in the Departments of Mechanical Science & Engineering and Aerospace Engineering. See http://fperc.uiuc.edu/
Parkinson’s Gait Initiation Study
E.T. Hsiao-Wecksler, C. MacKinnon
Parkinson’s disease (PD) has been estimated to affect 5 million people worldwide, 1 million in the United States alone. Two of the most devastating symptoms of PD, estimated to affect up to 50% of the population, include freezing of gait (FOG) and start hesitation. This simply means that a person with these symptoms has difficulty with successfully taking the first step. It has been recently demonstrated that these symptoms arise from an inability to properly coordinate a set of anticipatory postural adjustments (APAs) for gait initiation. Forms of external cueing such as auditory (music, rhythmic beeping), visual (objects, lines on the floor), and somatosensory (vibrating insoles) cues have been show to help elicit more normative APAs in persons with PD; however, the forces generated are under scaled in magnitude. In this study, we are investigating the utility of our portable powered ankle-foot orthosis (PPAFO) to provide active assistance at the ankle during gait initiation. Currently we are developing control strategies that more reliably elicit the necessary APAs for gait initiation. The ultimate goal of this project is to increase independence for people with PD who suffer from FOG and start hesitation by providing a dependable daily wear device to alleviate these symptoms.
Quantification of asymmetries in gait using shape analysis and multivariate statistical techniques
E. T. Hsiao-Wecksler, J. D. Polk, S. Hong, H. Dankowicz, K. S. Rosengren
Acute lower limb injury may lead to chronic gait problems or even disability due to asymmetry between the injured and uninjured limb. Current clinical gait analysis techniques used for diagnosis and rehabilitation are qualitative in nature and do not quantitatively assess recovery. The overall goal of this project is to develop quantitative techniques to assist in the treatment and monitoring of lower limb injury and asymmetry. Gait is a dynamic behavior with considerable changes in joint and body positions throughout the gait cycle. We are developing a novel technique, Integrated Multivariate Motion Analysis (IMMA), to distinguish asymmetry in gait and identify the source of asymmetry. IMMA uses geometric shape analysis (Generalized Procrustes Analysis) with multivariate statistical techniques (Principal Components Analysis and Parallel Factor Analysis) to capture the dynamic nature of walking behavior that current univariate measures cannot capture. This is a collaborative project with faculty in the Departments of Kinesiology & Community Health, Psychology, and Anthropology.
Effect of SCBA bottle configuration on gait and balance performance among firefighters
E. T. Hsiao-Wecksler, G. Horn, K. S. Rosengren

As first responders to emergency situations, firefighters play a crucial role in homeland security. Therefore, providing support to these first responders by examining human factors issues to improve their health and safety is of critical national importance. Falls and loss of balance on the fireground are one of the leading causes of traumatic injuries among firefighters, resulting in ~11K injuries per year (i.e., over 1/4 of all annual fireground injuries). Many of these events are potentially preventable; however, research examining the underlying mechanisms leading to these events and efforts to develop intervention programs to prevent falls have been limited. Along with the Illinois Fire Service Institute (IFSI) at UIUC, we are developing a research program to explore how firefighting equipment and environment affect balance, locomotion, and slip, trip, or fall (STF) risk. The overarching goal of this program will be to improve firefighter safety by reducing preventable STFs and provide knowledge that will aid in the choice and design of better firefighting gear. Specifically, we are examining how the addition of personal protective equipment (PPE), which consists of coat, pants, gloves, boots, helmet, hood, and self contained breathing apparatus (SCBA), affects STF risk through modification of gait and balance performance.
Postural control during mild impulsive perturbations
E. T. Hsiao-Wecksler
Investigating how individuals respond to disturbances to balance is essential to improving our understanding of the etiology of falls. Balance and postural control mechanisms during perturbed stance may change with age. These differences may manifest themselves in the behavioral characteristics of the postural response noted immediately after a perturbation. We are particularly interested in the response of the postural control system after a transient perturbation. Limited work has been done to explore postural responses to sudden, impulse-like perturbations. In this investigation, the impulse loading and impulse response control-theory paradigm will be used to examine the postural response to a mild, quick-release backward tug. While impulse response and its associated characteristics are rudimentary concepts in engineering control theory, we have only just begun to extend this paradigm to investigate postural control. The purpose of this study is to learn more about how to characterize responses to a transient perturbation, what these responses tell us about the postural control system in general, and how these responses may vary with age.
Tracking falls and fall-related events throughout the lifespan
E. T. Hsiao-Wecksler, K. S. Rosengren
Much of the research related to falls in older adults has used retrospective self-reports of falls over the previous 6 months or year. We are developing a prospective slips, trips, and falls survey (STAF Inventory) to better establish the incident rate of falls and fall-related behaviors. This survey evaluates the number of fall-related incidents as well as the environmental conditions, individual factors, and whether any injuries have occurred over a given study period.. Falls and fall-related events are being tracked for a period of 30 days. The STAF inventory is being administered to college-aged, middle-aged, and older adults. This is a collaborative project with faculty in the Departments of Kinesiology & Community Health, and Psychology.
Gait Analysis of Labrador Retrievers with Cranial Cruciate Ligament Deficiency
E. T. Hsiao-Wecksler, D. J. Griffon, G. J. Pijanowski
Cranial cruciate ligament (CCL) rupture is one of the most common injuries to the canine hind knee and is the leading cause of degenerative changes in that joint. Stress injuries are believed to result from a combination of conformation characteristics within the entire limb, resulting in a biomechanical imbalance between forces acting on the cranial tibial thrust. However, the exact role of each of these factors and their significance in relationship with CCL deficiency has not been defined. The objective of the current study is to examine whether there are distinct differences in the kinematics and kinetics of gait in healthy and injured Labrador Retrievers. To perform the gait analysis, we are collecting motion data which will be augmented with segment parameter data derived from CT and radiographic images of each animal’s limb. Our long-term goal is to develop a mathematical model integrating a combination of morphometric parameters to estimate the risk of developing CCL deficiency in each dog. This is a collaborative project with the College of Veterinary Medicine at the U of I.
News Gazette article: Scientists study cause of canine knee ailments
Effect of Tai Chi on balance and movement strategies
E. T. Hsiao-Wecksler, K. S. Rosengren
Tai Chi has been promoted to older adults as an exercise to improve physical and mental fitness. It has also been found to reduce the likelihood of falling in senior citizens. This project explored how Tai Chi experience may modify postural control mechanisms and movement strategies specifically during unexpected external perturbations to balance and while walking over level ground and obstacles. We are also investigating new techniques for assessing Tai Chi skill proficiency. We conducted both cross-sectional studies on individuals with long-term Tai Chi experience (> 2 yrs) and longitudinal studies on older adults who received Tai Chi training for 5 months. This is a collaborative project with faculty in the Departments of Kinesiology & Community Health, and Psychology.
Video of motion capture of obstacle crossing
Video of motion capture of Tai Chi skill assessment
Optimization-Based Inverse Dynamics to Reduce Errors in Estimated Joint Torques
E. T. Hsiao-Wecksler
Inverse dynamics is a powerful tool for the biomechanical analysis of human movement, and is commonly used to calculate the net torques generated in various limb joints. Despite the widespread use of this method, past research has shown that the errors in joint torque calculations are relatively large. These errors are attributed to inaccuracies in the input variables of the inverse dynamics equations. We have determined that the primary contributor is inaccuracy in the measured motion (e.g., segment angle profiles), and the secondary contributors include inaccuracies in estimations of body segment parameters (i.e., mass, center of mass location, moment of inertia). To improve the accuracy of inverse dynamics estimations, it is necessary to find techniques to reduce the effects of these error sources. We propose the development of an optimization-based approach that can accommodate errors due to both measured motion and body segment parameters. The development of the optimization-based approach will include several studies. The proposed approach has the potential to change the way joint torque estimations are made, and will lead to better clinical and research tools for the analysis of human movement.
Biomechanical analysis of aggressive in-line skating: landing and balance on grind rail
E. T. Hsiao-Wecksler, P. Kurath
Aggressive in-line skating is a sport that emphasizes balance. A popular activity is grinding, where the skater jumps onto a grind rail — which may be a specially designed structure at a skatepark, or a common handrail on a staircase. In grinding, skaters jump up and accurately place their skates on the rail, smoothly decelerate, and balance upon the rail while sliding (or “riding it out”). In-line skaters have developed a heuristic approach to training. Inherent to their training are exercises that emphasize the development of muscle control during eccentric, muscle stretching, contractions to smoothly decelerate the body. For example, before performing a grind, the skater would repeatedly jump upon an object and “stall” — that is, jump, place skates on the rail, decelerate, and hold that position. In this novel study, we collected data on limb motion and forces developed during deceleration activities, such as grinding and stalling. By performing controlled jumping and balancing experiments, this project allowed us to gain insight into how these individuals are able to use eccentric contraction to assist with maintaining balance and, perhaps, minimizing impact force and energy.
Video of motion capture.
Variations in balance and postural control throughout pregnancy and up to 6 months postpartum
E. T. Hsiao-Wecksler
Pregnant women ancedotally state that balance changes as pregnancy progresses and the circumference of the trunk and body weight increase. However, no studies have examined how balance, and postural control that moderates balance, may vary throughout pregnancy and the subsequent postpartum period. This study assessed how balance and postural control varied as a consequence of pregnancy by examining how a subject’s postural sway varied over the 9 month pregnancy and a following 6 month postpartum period.